

In the United Kingdom, chemical labelling requirements are governed by the Classification, Labelling and Packaging (CLP) Regulation (GB CLP), which aligns with the Globally Harmonised System (GHS) and is enforced under UK REACH
Labels are an important part of hazard communication, they provide critical information to protect workers from chemical exposure risks. Understanding the difference between primary and secondary container labels is critical for compliance with GB CLP and helps keep employees safe.
What Is a Primary Container Label?
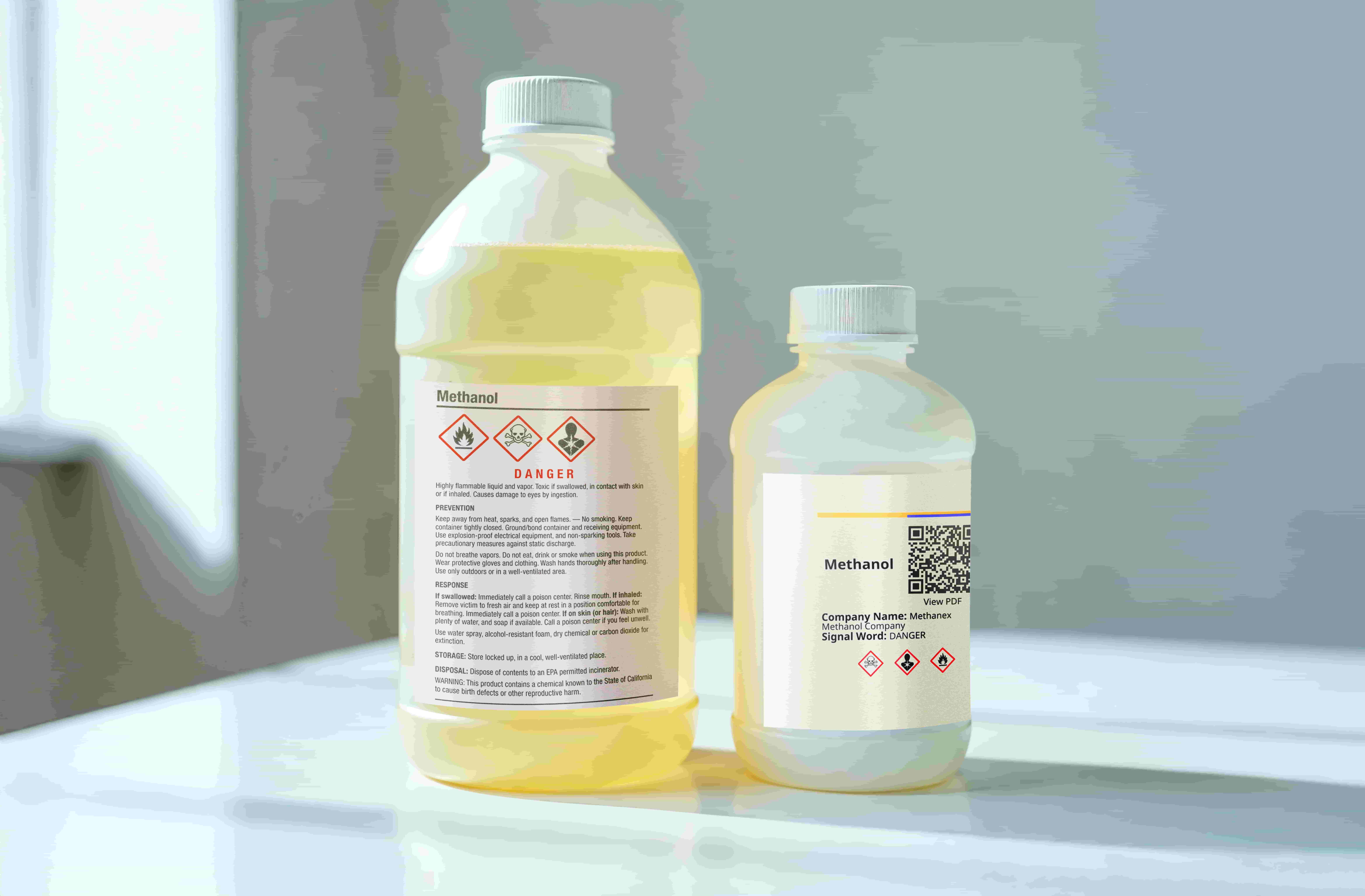
A primary container label is the original label provided by the manufacturer, importer, or distributor on the container in which the chemical is shipped.
GB CLP Requirements for Primary Labels: Must include all GHS label elements.
- Product identifier – Matches the name in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
- Supplier information – Name, address, and phone number of the responsible party
- GHS pictograms – For all applicable hazard classes
- Signal word – “Danger” or “Warning”
- Hazard statements – Standardized descriptions of hazard types and severity
- Precautionary statements – Guidance on safe handling, storage, and disposal
- Supplemental information – Where required under GB CLP.
Example: A gallon of paint thinner shipped from the manufacturer with a label containing the flammable pictogram, “Danger” signal word, and hazard/precautionary statements.
What Is a Secondary Container Label?
A secondary container label is used when a chemical is transferred from its primary container into another container for use within the workplace.
When Required Under UK Law
Every workplace container holding a hazardous substance must be clearly labelled unless:
- The chemical is used immediately by the employee who transferred it, and
- The container remains under their direct control and supervision at all times.
Minimum Requirements for Secondary Labels
At a minimum, secondary container labels should include:
- Product identifier – Consistent with the SDS.
- Hazard information – Words, symbols, or pictograms giving general hazard awareness.
Best practice (recommended by the HSE): Include relevant pictograms, signal words, and hazard statements for clarity and consistency.
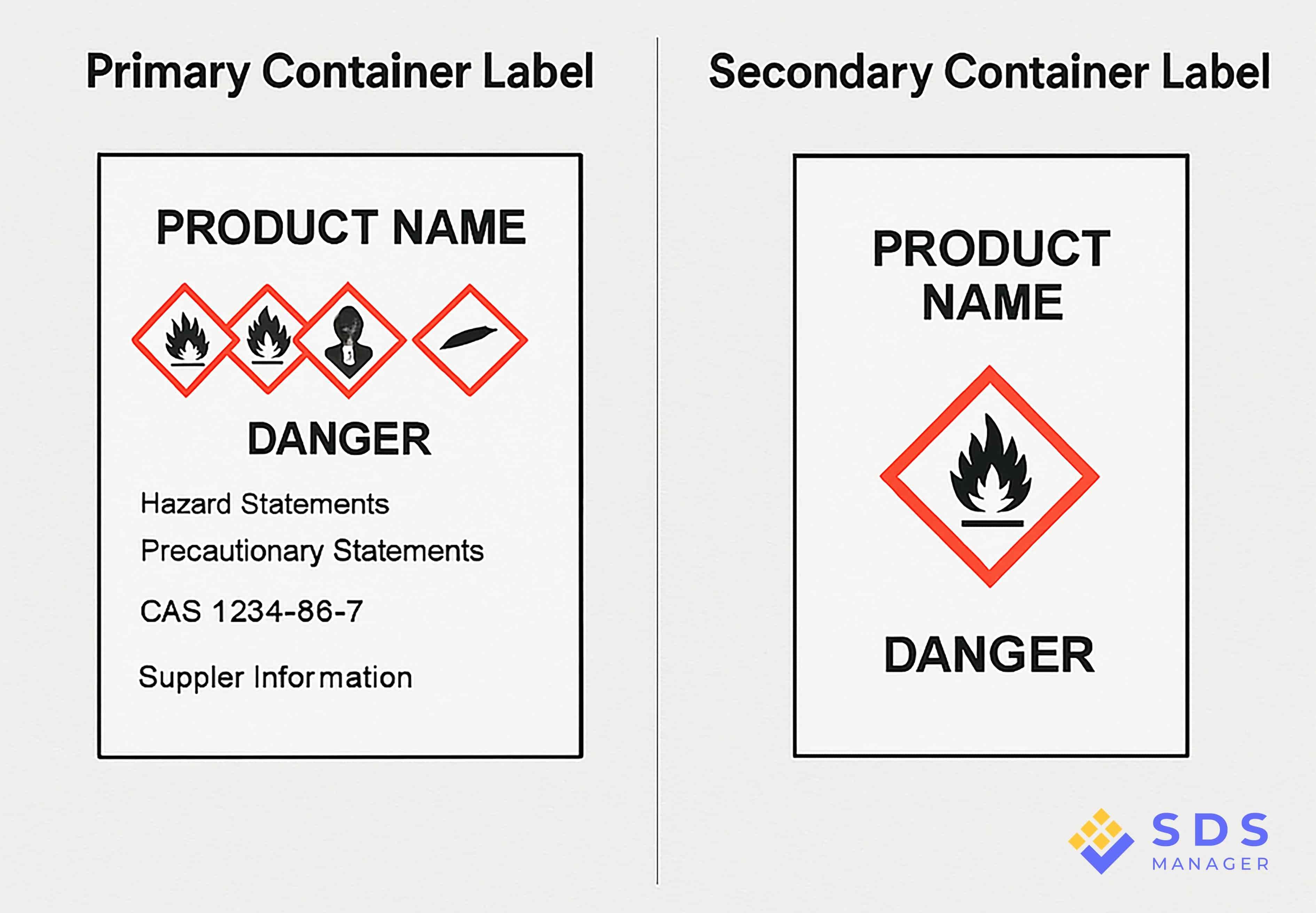
Key Differences Between Primary and Secondary Labels
| Differences | Primary Container Label | Secondary Container Label |
|---|---|---|
| Created and Applied By | Manufacturer, importer, or distributor | Employer or workplace staff transferring the chemical |
| Content | Full GB CLP label (product ID, supplier info, pictograms, hazard & precautionary statements) | Minimum: product ID + hazard information; Recommended: pictograms, signal words, hazard statements |
| Purpose | Communicate full hazard and regulatory information to any handler | Communicate hazards to employees in the workplace |
| When Required | On all shipped chemical containers | On all workplace containers not used immediately by the person who filled them |
| Regulatory Basis | GB CLP Regulation under UK REACH | GB CLP workplace labelling guidance (HSE) |
Common Workplace Compliance Mistakes
- Leaving secondary containers unlabeled when shared or stored for later use
- Using abbreviations or chemical codes that employees can’t understand
- Not matching the product name to the SDS exactly
- Failing to update labels when chemical formulations or hazards change
The Easy Way to Stay Compliant
Manual creation of compliant secondary labels can be slow and error-prone. SDS Manager’s free GHS Secondary Label Generator allows you to:
- Auto-fill hazard information directly from your SDS
- Support multiple label sizes and layouts
- Add GHS pictograms and hazard statements automatically
- Include QR codes linking directly to the SDS for instant access
With automation, you can maintain compliance, save time, and reduce labeling errors across your workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is the main difference between primary and secondary container labels?
A: Primary labels are provided by the manufacturer and include full GHS information; secondary labels are applied in the workplace when chemicals are transferred into another container.
Q. Do all secondary containers need a label?
A: No. If the container is used immediately by the person who filled it and never leaves their control, labeling is not required. Otherwise, it must be labeled.
Q. Can I handwrite secondary container labels?
A: Yes, as long as they are legible, durable, and include required hazard information.
Q. Do secondary labels need pictograms?
A: While not always legally required, HSE recommends including them for clarity and safety..
Q: How can I make sure my labels are GB CLP-compliant?
A: Use the product’s SDS for accurate information, ensure the label matches GB CLP requirements, and follow HSE workplace guidance.